Diet Research Data:Effects of Long-Term High Fat Diet 32 Feeding on Male Wistar Hannover Rats
4.Fasting blood glucose levels
6.Weights of major organs at Biopsy
8.Adiponectin and leptin concentrations at Biopsy
9.Liver and adipose tissue observation
Related CLEA Japan product: High Fat Diet 32

For the animal, please click here↓![]() : https://www.clea-japan.com/en/products/general_diet/item_d0080
: https://www.clea-japan.com/en/products/general_diet/item_d0080
Inquiry:
If you have any question, please feel free to contact us from here.
1.Objective
The aim of this study was to collect basic data and data on obesity- and diabetes-related lesions (such as hyperglycemia and complications) that are expected to develop due to long-term feeding of a high-fat diet by conducting a 50-week long-term high-fat diet feeding study in rats.
2.Materials and Methods
(1)Experimental Site
The experiment was conducted in the rat and mouse breeding facility (conventional) of Nippon Compound Feed Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (currently Feed One Co., Ltd.) Central Research Laboratory.
(2)Diets
- Low Fat Diet (LFD): Crude fat content 4.5%, Fat kcal% 10.8%, soluble non-nitrogenous substance content 64.3%, NFE kcal% 68.8%
- High Fat Diet 32 (HFD32): Crude fat content 32.4%, Fat kcal% 57.4%, soluble non-nitrogenous substance content 29.1%, NFE kcal% 22.9%
(3)Animals
Male BrlHan: WIST@Jcl (GALAS) rats (Wistar Hannover rats) were used.
(4)Housing Conditions
- Temperature and humidity: Temperature = 21-25°C, Humidity = 40-60%
- Lighting: 12-hour light/12-hour dark cycle (lights on 9:00 AM - 9:00 PM)
- Cages: Two rats were housed per polypropylene rat cage (345× 403× 177mm)
- Diet: Ad libitum
- Drinking water: Ad libitum tap water
(5)Experimental Procedure
Experimental animals were introduced at 4 weeks of age and acclimatized for 1 week (fed CE-2). After acclimatization, animals were divided into groups based on body weight and blood glucose levels. The experimental diets were fed from 5 weeks of age. Six rats per group were sacrificed at 30 weeks of age, and the remaining 8 rats were sacrificed at 55 weeks of age. After a 15-hour fast, animals were anesthetized with isoflurane and sacrificed for organ weight measurement and blood analysis. Blood glucose levels were measured using a GlucoTest PROR (Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd.). Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t-test.
3.Results
The results are described below.
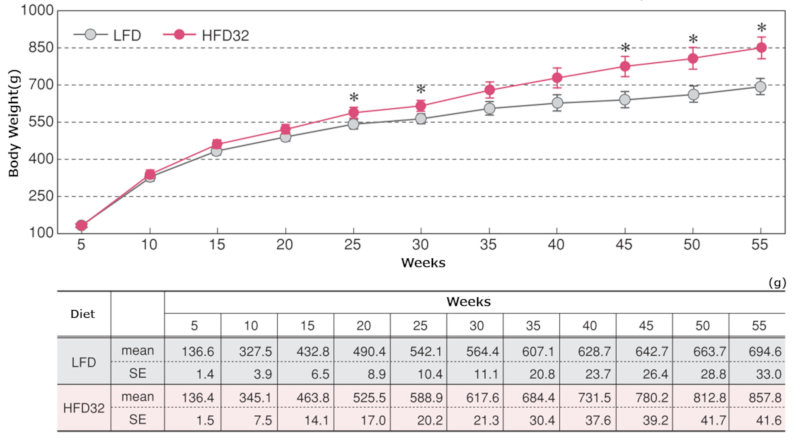
1.Body Weight
Changes in body weight
Data are presented as mean ± standard error. Statistical analysis was performed between groups at each time point, and an asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05).
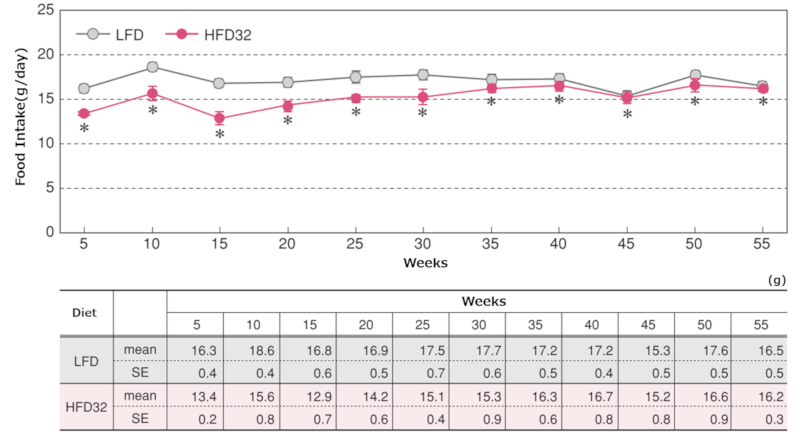
2.Food Intake
Changes in food intake
Data are presented as mean ± standard error. Statistical analysis was performed between groups at each time point, and an asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05).
3.Random Blood Glucose Levels
Changes in random blood glucose levels
Data are presented as mean ± standard error.
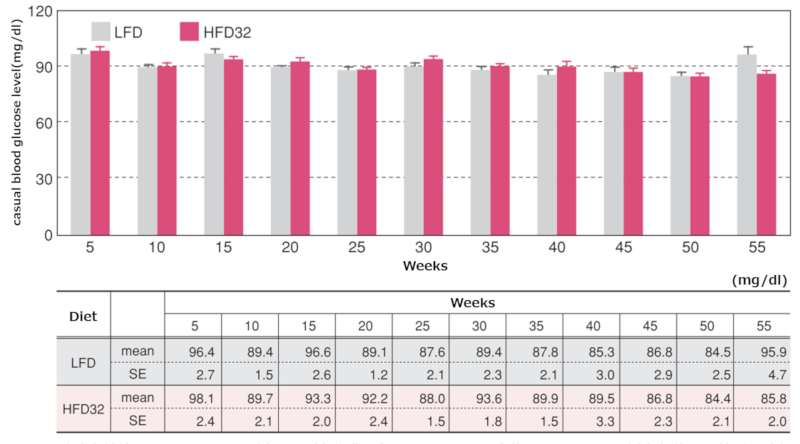
Random blood glucose levels were measured every 5 weeks, always at 1:00 PM. Blood was collected from the tail vein, and a whole blood glucose meter (GlucoTest PROR, Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd.) was used for the measurement.
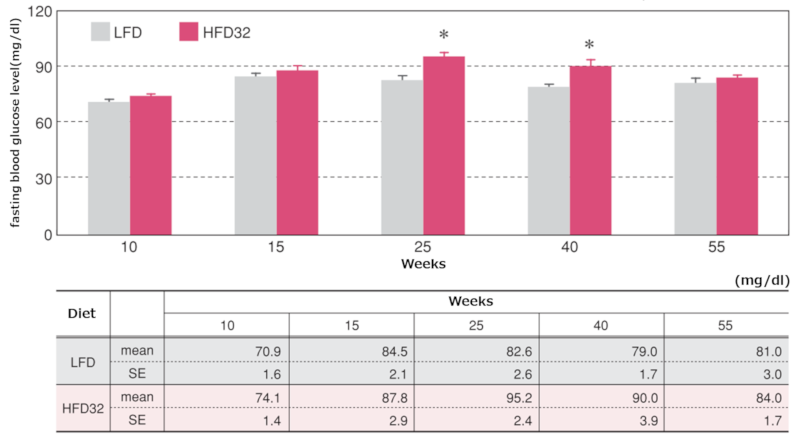
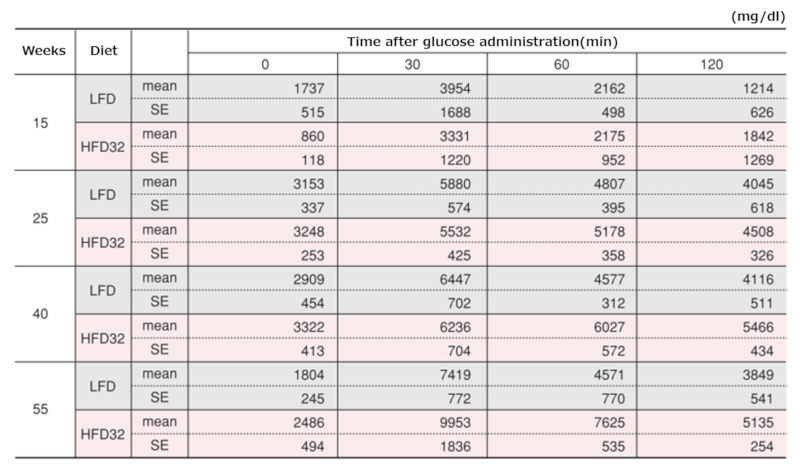
4.Fasting Blood Glucose Levels
Changes in fasting blood glucose levels
Data are presented as mean ± standard error. Statistical analysis was performed between groups at each time point, and an asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05).
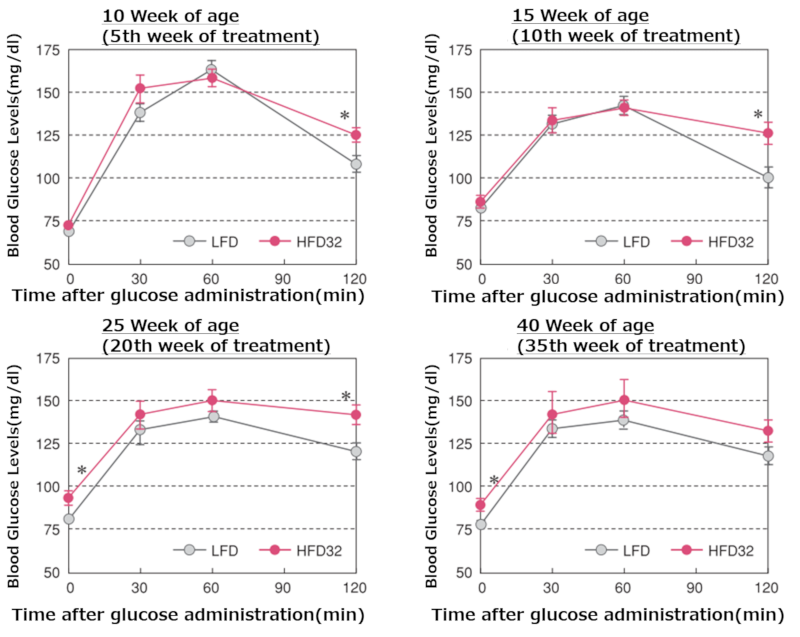
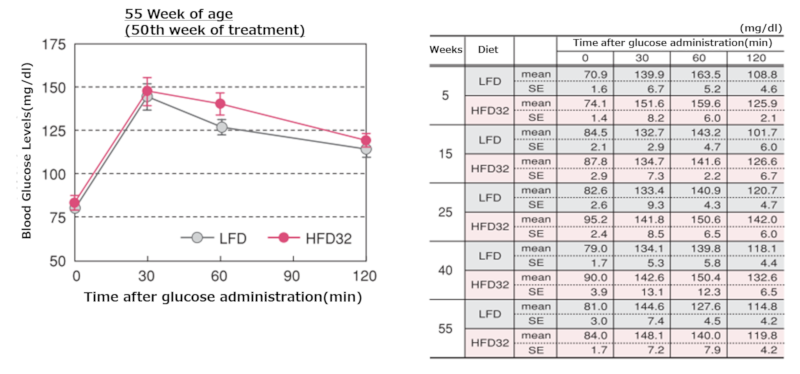
5.Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
Oral glucose tolerance test results at each time point
Upper left figure; 10 weeks, Upper right figure; 15 weeks, Middle left figure; 25 weeks, Middle right figure; 40 weeks, Lower left figure; 55 weeks
Data are presented as mean ± standard error. Statistical analysis was performed between groups at each time point, and an asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05). After a 15-hour fast, glucose was orally administered (2g/kg body weight), and blood glucose levels were measured 30, 60, and 120 minutes after administration.
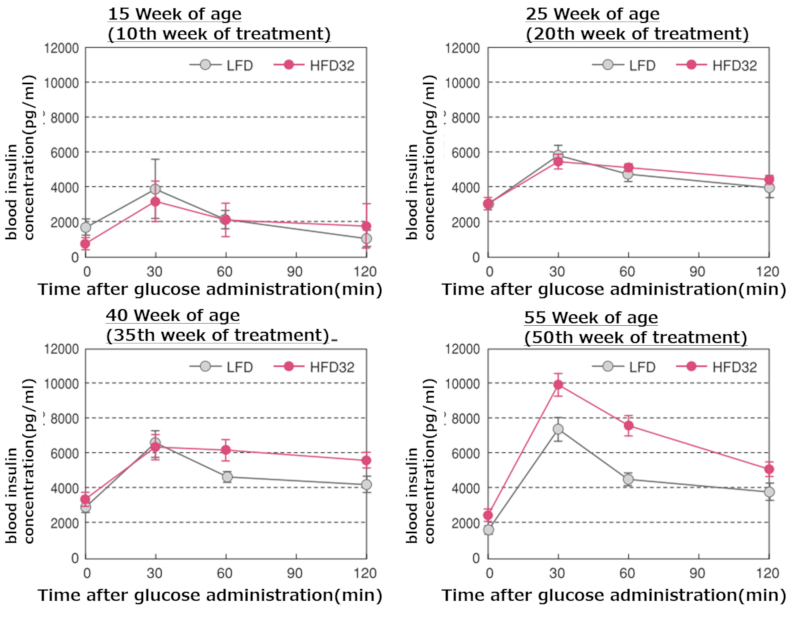
Plasma insulin concentrations during the oral glucose tolerance test at each time point
Upper left figure; 15 weeks, Upper right figure; 25 weeks, Lower left figure; 40 weeks, Lower right figure; 55 weeks
Data are presented as mean ± standard error. Statistical analysis was performed between groups at each time point, and an asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05). Blood samples were collected simultaneously with blood glucose measurements during the oral glucose tolerance test, and plasma was obtained by centrifugation for insulin measurement. An ELISA Insulin kit (Morigana Seikagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd.) was used for insulin measurement.
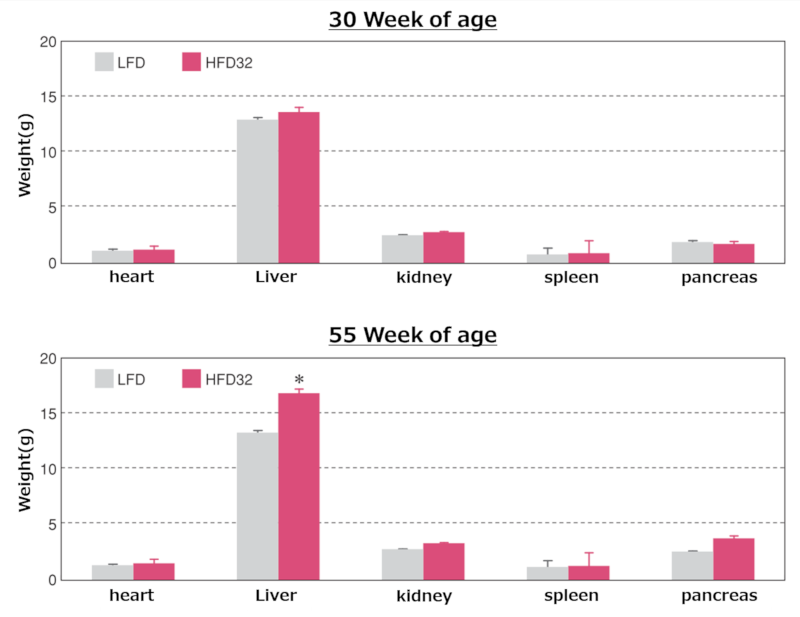
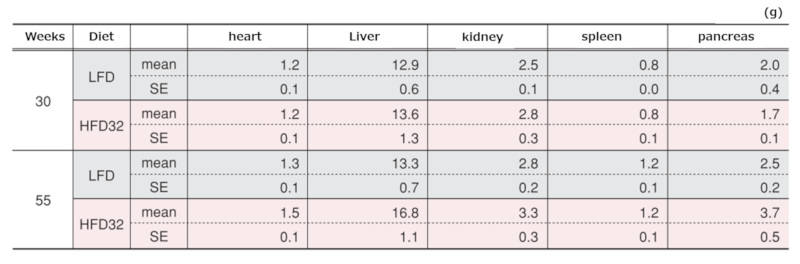
6.Weights of Major Organs at Biopsy
Weights of major organs at each time point
Data are presented as mean ± standard error. An asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05). Animals were fasted for 15 hours before Biopsy.
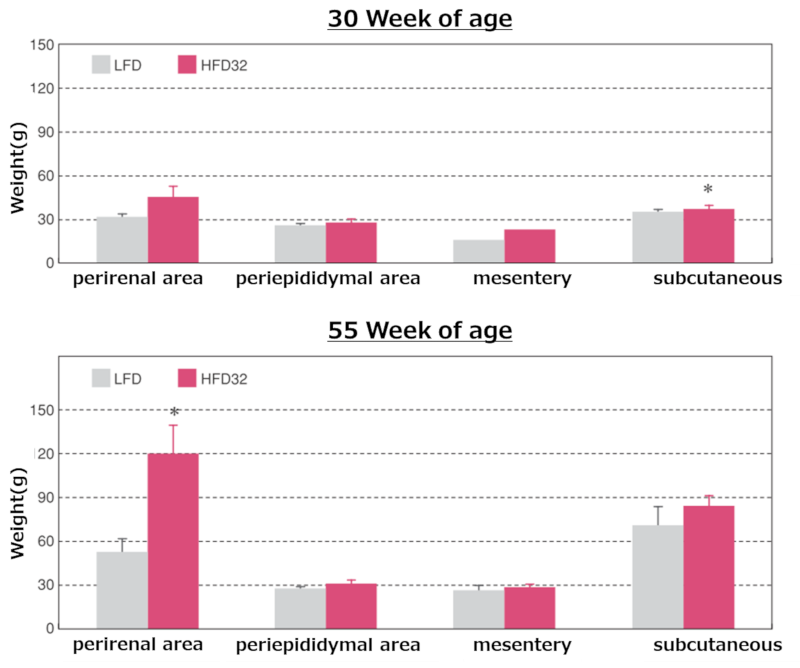
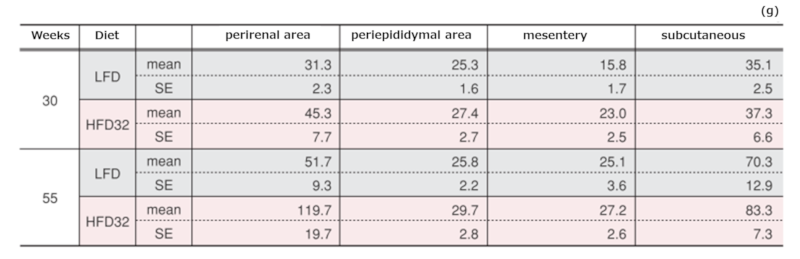
Weights of regional adipose tissue at each time point
Data are presented as mean ± standard error. An asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05). Animals were fasted for 15 hours before Biopsy.
7.Blood Analysis at Biopsy
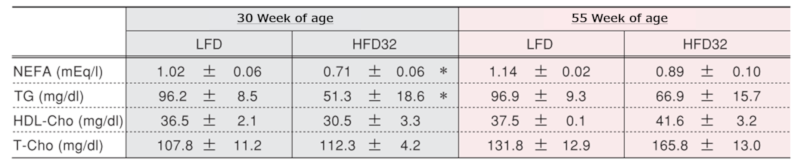
Changes in serum lipid-related substances at each time point
Values in the table represent the mean ± standard error. An asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05).
NEFA: non-esterified fatty acids, TG: triglycerides, Cho: cholesterol, T-Cho: total cholesterol
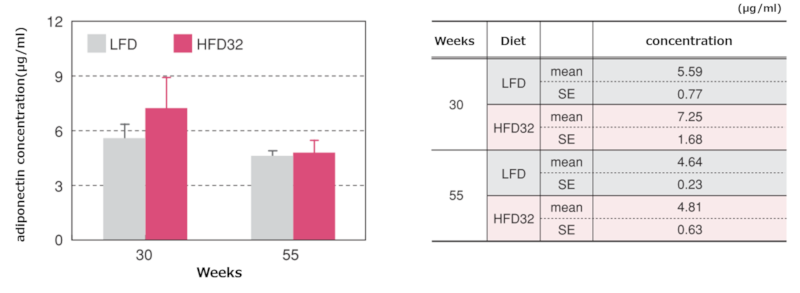
8.Adiponectin and Leptin Concentrations at Biopsy
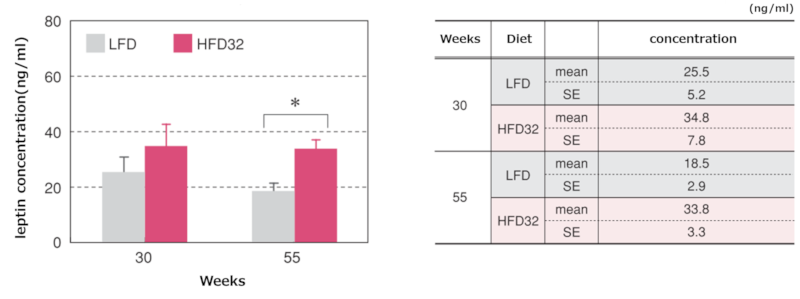
Plasma leptin concentrations at each time point
Data are presented as mean ± standard error. An asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05). Blood was collected from the posterior vena cava at Biopsy, and plasma was obtained by centrifugation for leptin measurement. A Leptin/Rat ELISA kit (Morigana Seikagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd.) was used for leptin measurement.
Serum adiponectin concentrations at each time point
Data are presented as mean ± standard error. Blood was collected from the posterior vena cava at Biopsy, and serum was obtained by centrifugation for adiponectin measurement. A mouse/rat adiponectin ELISA kit (Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) was used for adiponectin measurement.
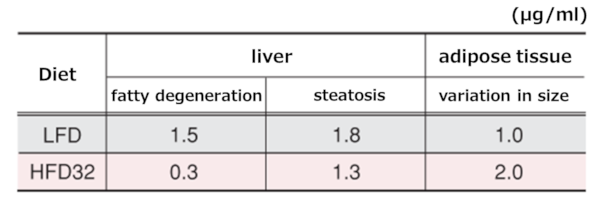
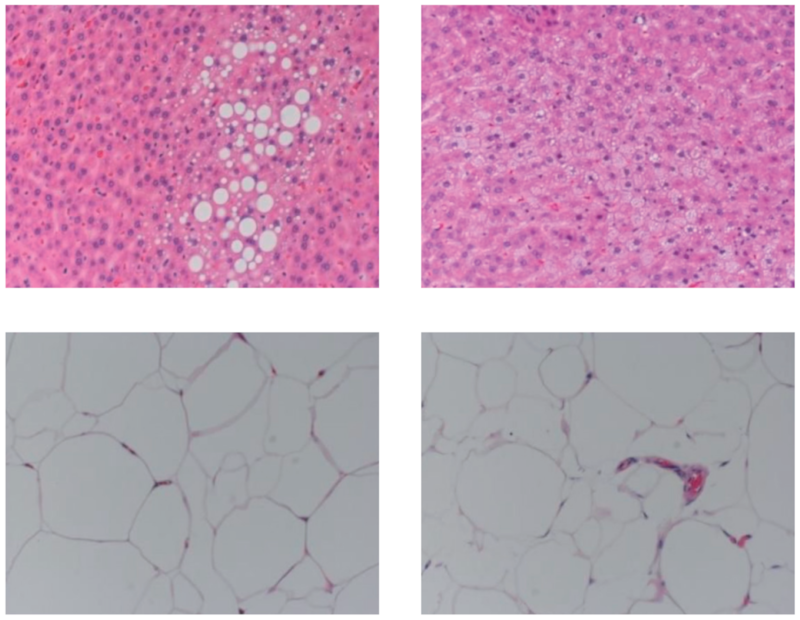
9.Liver and Adipose Tissue Observation
Histological images of liver and adipose tissue at 55 weeks of age (HE staining, ×300)
Upper left: LFD group liver, Upper right: HFD32 group liver, Lower left: LFD group adipose tissue, Lower right: HFD32 group adipose tissue
Liver: In the LFD group, relatively large lipid droplets were observed in the liver tissue, whereas in the HFD32 group, small lipid droplets were observed within the cells.Adipose tissue: In the LFD group, relatively well-shaped adipocytes were observed, while in the HFD32 group, many cells had irregular shapes and a mixture of large and small cells.
Evaluation of liver and adipose tissue
A score was assigned based on the "frequency" and "severity" of findings: 0: no evidence, 0.5: rare/slight, 1: slight = 1, 1.5: slight~moderate, 2.0: moderate, 2.5: moderate~severe, 3.0: severe.
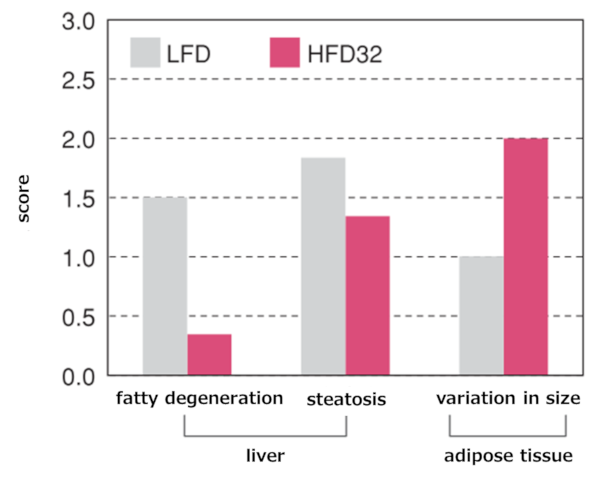
Results of tissue evaluation
Note: Fatty degeneration refers to findings where hepatocytes are degenerated and necrotic accompanied by fat accumulation. Fatty droplet degeneration refers to findings where large and small lipid droplets are deposited in the cytoplasm.