ODS/ShiJcl-od/od
Animals/Other Disease Models and Germ-Free Animals/

Ordering name: ODS/ShiJcl-od/od
Nomenclature: ODS/ShiJcl-Gulood
Availability: Live colony
Not genetically modified animal
Origin & Characteristics
Origin
Dr. Susumu Makino and his colleagues found several animals that had gait abnormalities among Wistar-Shionogi rats that they were maintaining. They named these animals osteogenic disorder (OD) rats because they exhibited prominent bone and joint abnormalities and systemic bleeding. Subsequent studies revealed that these symptoms were derived from an ascorbic acid (vitamin C) deficiency arising from defective gulonolactone oxidase (GLO) activity. This characteristic was confirmed to be the result of a mutation involving the autosomal single recessive gene od. As part of a contract with Shionogi & Co., Ltd., the production and supply of this strain was begun. denotes the origin from Shionogi & Co., Ltd.
Characteristics
In a state of vitamin C deficiency, rats develop a gait abnormality, poor food intake, weight loss, bleeding from systemic tissue (scorbutic state), systemic dysostosis, multiple bone fractures, osteoporosis, etc., resulting in death.
Use
- Studies on metabolism and excretion of xenobiotics (various chemical substances, drugs, etc. for human) and cholesterol
- Nutritional physiological investigations of the brain
- Studies on antiviral and antitumor effects
- Studies on scurvy and various bone abnormalities
Methods of production and maintenance
The ODS/ShiJcl-od/od strain is produced by mating od/od males x females, and the ODS/ShiJcl-+/+ strain is produced by mating +/+ males x females. Breeding is performed in accordance with the method used for other inbred rat strains. These rats are given autoclaved CE-2 and water containing chlorine (4 - 6 ppm) and L-ascorbic acid (1g/500cc) ad libitum.
Onset of deficiency, survival period, and changes in weight in ODS/ShiJcl-od/od rats
Animals given water containing L-ascorbic acid (1 mg/mL) and solid food (CL-2: vitamin C-free) ad libitum until 5 weeks were reared using water containing no L-ascorbic acid, and the incidence of an abnormal appearance within the next 30 days, the number of days until all the animals had died, and the body weights were determined.
Appearance findings
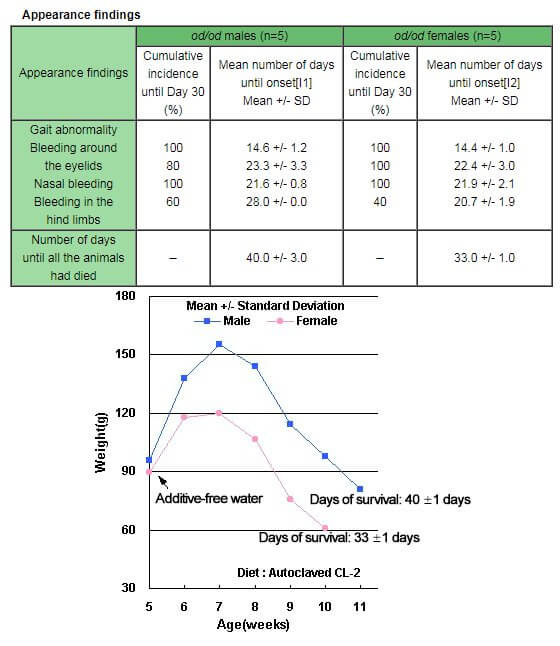
Onset of deficiency, survival period, and changes in weight in ODS/ShiJcl-od/od rats
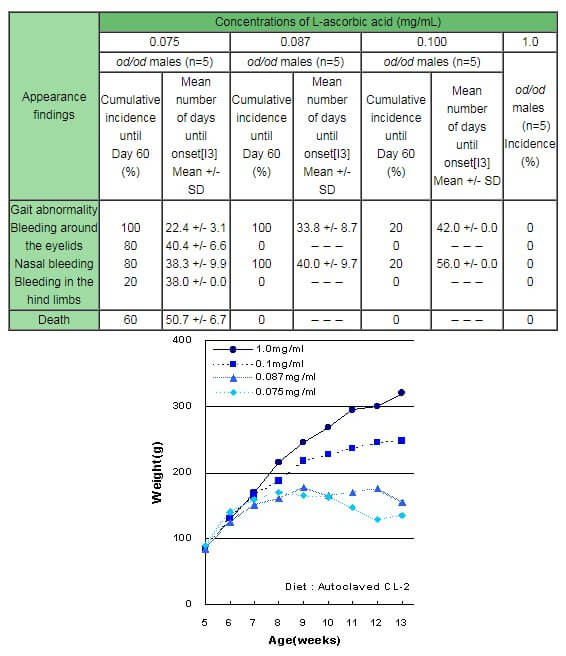
Onset of deficiency, days of survival, and changes in body weight in ODS-ShiJcl-od/od rats Rats given water containing L-ascorbic acid (1 mg/mL) and solid food (CL-2: vitamin C-free) ad libitum until 5 weeks were reared for 60 days with water containing four different concentrations of L-ascorbic acid (0.075 mg, 0.087 mg, 0.100 mg, or control 1.0 mg per mL of tap water), and the appearance findings and changes in body weight in these groups of rats were determined.
Appearance findings
Genetic profile
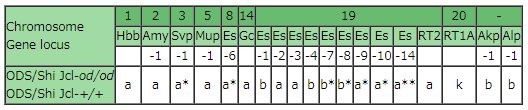
*:Only male **:Only female
Our Contract Research Services related with This Animal
For details on our contract research services, including cryopreserved embryos, contracted testing, and the provision of research materials such as blood and organs, please click here .


