KK-Ay/TaJcl
Animals/Diabetes Models/

Ordering name: KK-Ay/TaJcl
Nomenclature: KK.Cg-Ay/TaJcl
Availability: Live colony
Not genetically modified animal
Characteristics
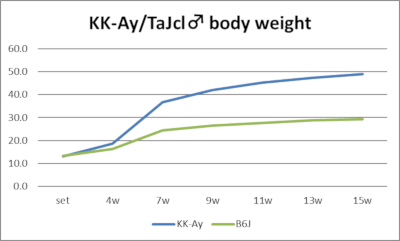
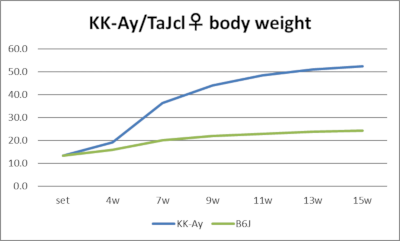
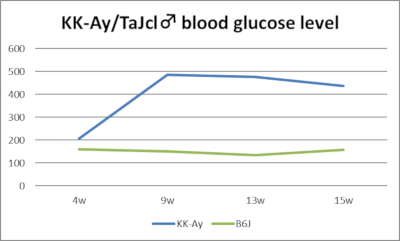
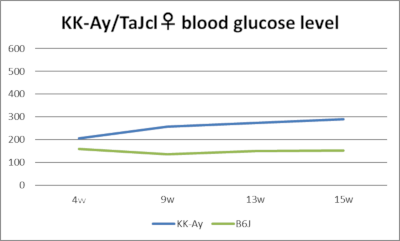
KK-Ay mice are a combined model created by backcrossing the natural obesity gene Ay into KK mice. They develop obesity and hyperglycemia earlier (7-8 weeks of age) and more severely than KK mice. Females, in particular, exhibit marked obesity, exceeding the weight of males around 8 weeks of age. The Ay gene is a dominant gene located on chromosome 2 and is a natural mutation gene with pleiotropic effects, including obesity, hyperglycemia, coat color, and lethality (Ay / Ay).
Male KK-Ay mice are individually housed from 7 weeks of age to prevent fighting-related injuries.
Coat color gene : aa BB CC DD (yellow)
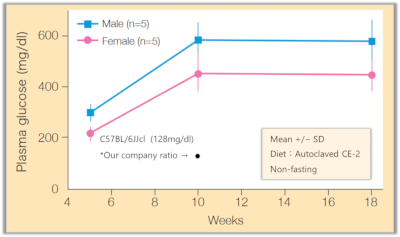
2023 Aggregate Data
Body weight and blood glucose trends (male/female, 2023 aggregate data)
Origin
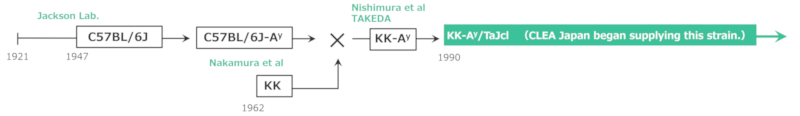
Around 1910:
Mice were bred as pets in Kasukabe area, Saitama Prefecture, and strains such as KK, KA1, KB2, and KSA were established from the Kasukabe-derived mice.
1962:
Kondo et al. discovered mice exhibiting obesity and hyperglycemia within a tail-kink spontaneous mutant line (K line) of the K strain (Kasekabe) that they had been maintaining for genetic studies. This line attracted attention as a model of non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Nishimura et al. introduced the Ay gene, which exhibits multiple phenotypes such as lethality, yellow coat color, and obesity, into KK mice, creating KK- Ay mice that developed obesity and hyperglycemia earlier and more severely than KK mice.
1963:
Both KK and KK-Ay mice were introduced to Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.
1990:
The mice introduced from Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited began to be produced and supplied as KK/TaJcl and KK-Ay/TaJcl.
Cautions for the Breeding and Experimentation of Diabetic Model Animals
- Acclimation: Please take 3-5 days of acclimation after transportation to avoid hypoglycemia caused by stress.
- Individual Housing: KK-Ay mice should be individually housed to prevent increases in blood glucose levels due to fighting when group-housed.
- Frequent Bedding Changes: Due to polyuria associated with diabetes, please increase the frequency and amount of bedding changes.
- Consistent Measurement: Blood glucose levels can fluctuate based on diet, measurement methods, and sample type (blood, serum, plasma). Please ensure consistent procedures.
Our Contract Research Services related with This Animal
For details on our contract research services, including cryopreserved embryos, contracted testing, and the provision of research materials such as blood and organs, please click here .
FAQ
What is KK-Ay/TaJcl?
KK-Ay/TaJcl is a type 2 diabetes model mouse created by backcrossing the natural obesity gene Ay into KK mice. It develops obesity and hyperglycemia earlier (7-8 weeks of age) and more severely than KK mice.
Is KK-Ay/TaJcl genetically modified?
No. KK-Ay/TaJcl is a Not genetically modified animal.
What are the key phenotypic characteristics of KK-Ay/TaJcl?
KK-Ay/TaJcl exhibits obesity, hyperglycemia, yellow coat color, and pleiotropic effects associated with the dominant Ay gene located on chromosome 2. Females show marked obesity, exceeding male body weight around 8 weeks of age.
What is KK-Ay/TaJcl used for?
KK-Ay/TaJcl is used for screening anti-hyperglycemic drugs and for the analysis and elucidation of diabetic complications.
What precautions should be taken when breeding KK-Ay/TaJcl?
Please allow 3-5 days of acclimation after transportation. Male KK-Ay mice should be individually housed to prevent fighting-related increases in blood glucose levels. Increase bedding changes due to polyuria and ensure consistent blood glucose measurement procedures.